This article is part of TPM Cafe, TPM’s home for opinion and news analysis. It was originally published at The Conversation.
It may seem that the midterm elections are firmly behind us.
Pollsters are already measuring likely outcomes in 2024 presidential matchups. And announced candidates and possible contenders for the Republican presidential nomination are taking trips to Iowa, the party’s first nominating state.
But 2022 election results from two key states tell us a lot about how voting laws and issues on the ballot influence the way people vote.
At first glance, it’s not easy to understand why Michigan, a left-leaning swing state, and Ohio, a Republican stronghold and former swing state, had such different electoral outcomes in the midterms. Their similar demographic makeups and past similar voting patterns – such as electing Republicans statewide over several election cycles – suggest they would tend to have similar results at the ballot box.
As scholars of electoral politics and state policy in Ohio, we explored recent elections in both states and found a divergence after 2016, with Michigan voting more blue and Ohio voting more red. Our analysis suggests differences in voter registration laws and ballot initiatives may explain why these two states have taken different electoral paths. This preliminary research has not yet been peer-reviewed.
Between 2000 and 2012, the states had similar voting results more than half the time. But they did diverge slightly. During the period, Michigan voters picked the Democratic presidential candidate in each of the four contests. Meanwhile, in Ohio, voters went twice each for Republican President George W. Bush and Democratic President Barack Obama. At the gubernatorial level, for three elections during this period – 2002, 2006 and 2010 – Michigan elected one Republican and elected and reelected one Democrat, while Ohio elected two Republicans and one Democrat.
In the 2016 presidential election, voters in both Michigan and Ohio chose Republican candidate Donald Trump. That year, there was no U.S. Senate election in Michigan, but Ohio voters returned Republican U.S. Sen. Rob Portman for another term. And voters in both states sent more Republicans than Democrats to the U.S. House of Representatives and both houses of their state legislatures.
While the two states had been slowly moving apart for a couple of decades, they converged in the 2016 presidential election for Trump.
Michigan goes blue, Ohio stays red
Since 2016, however, voters in the two states have followed drastically different political paths. In 2018, 2020 and 2022, Michigan voters elected Democratic candidates for governor, U.S. Senate and president as well as a majority in both houses of the state legislature. And they voted for ballot initiatives that legalized marijuana, reformed redistricting and legalized same-day voter registration, which included straight-ticket voting, automatic voter registration, same-day voter registration and no-excuse absentee voting. They also voted to modify the state constitution to protect abortion and contraception rights – all policies typically supported by Democratic candidates.
During the same three election cycles in Ohio, residents cast their ballots for Republican candidates and policy initiatives favored by Republicans. Voters rejected drug-related criminal justice reform, approved a referendum that could make bail more punitive and affirmed that only U.S. citizens could vote in Ohio elections. Republicans actually dominated electoral politics in both federal and state races, with one exception: in 2018, voters sent Democrat Sherrod Brown back to the U.S. Senate.
Beyond that, Ohioans voted for a Republican governor, presidential candidate, all statewide executive offices, in addition to the governor, the three open seats on the state supreme court and a super majority in the state legislature. The U.S. Senate seat vacated by a Republican stayed in Republican control.
It’s not demographics
Analysts suggest that Ohio is no longer a swing state because it is overwhelmingly white and working-class. But, as we examined the populations, we learned demographic differences were not the reason Michigan and Ohio voters diverged politically. Data from the American Community Survey, a demographic study from the U.S. Census Bureau, shows that these two Midwest states are remarkably similar demographically.
Michigan and Ohio have similar white populations, 78% and 80%, respectively; Black populations, 14% and 12%; bachelor’s degree recipients, both 18%; people over 65, both 17%; median household incomes, both $59,000 in 2020 dollars; and workers belonging to unions, 13% and 12%.
But state-specific exit polls of early and 2022 Election Day voters in Michigan and Ohio show there are differences in the electorate. Ohio voters were a little more likely to be male – 52% to 50% – and white, 83% to 80%, than Michigan voters.
Ohio voters were less likely to reside in a union household – 21% to 27% – and were much more likely to identify as Republicans, 41% to 32%.
Early voter registration may play a part
In 2018, Michigan approved same-day registration, which allows voters to register on Election Day, and automatic voter registration, which makes voter registration automatic with driver’s license applications and renewal for those eligible. Ohio requires voters to register nearly a month prior to Election Day.
Registration data for Michigan shows these easier methods of registration may have corresponded with higher voter participation in the state. The increase in total votes cast in Michigan, from 4.8 million in 2016 to 5.5 million in 2020, suggests the 2018 registration changes had an effect. While there may be other factors related to Michigan’s increased turnout, the changes in the state’s laws suggest same-day and automatic registration played a part.
What’s more, there was a higher number of registered voters in Michigan than in Ohio, even though Ohio has 1.7 million more people than Michigan. And, according to the Federal Register, Ohio has 1.3 million more residents of voting age than Michigan. The data also indicates Ohio historically had a larger number of registered voters than Michigan until Michigan approved same-day and automatic voter registration.
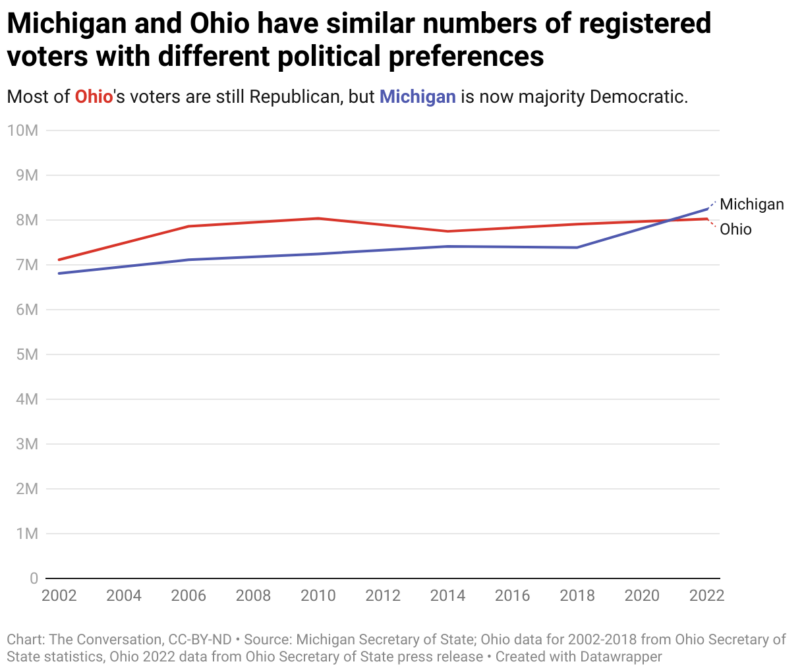
According to the Michigan secretary of state’s official election results, there were 4.5 million total votes in the gubernatorial election, the highest office contested in 2022. Meanwhile in Ohio, the secretary of state reported 4.2 million total official votes cast for governor.
Issues may affect voter participation
There is some indication that when social issues that people care about are on the ballot, more people vote. In 2022, Michigan had a proposal that called for adding the right to abortion and contraceptive use to the state constitution. That year, according to data from the Michigan secretary of state’s office, the total number of voters in the state was up by 159,060 from 2018. Ohio, though, had ballot issues in 2022 related to setting bail for criminal defendants and prohibiting noncitizens from voting in local elections. The total number of voters in Ohio dropped by 295,466 between 2018 and 2022.
Before candidates work to mobilize and persuade voters, campaigns try to influence the pool of potential voters, acting within the rules of their states. Changes in the registration rules in Michigan, along with social issues on the ballot and other factors, may have created a different electoral environment there than exists in Ohio, where none of these changes have taken place. This suggests the possibility that writing off Ohio as a noncompetitive state may be premature.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.







I found this article to be quite interesting; helps explain the importance to Republicans for limiting ballot access.
One phrase really caught my attention though. “Black populations, 14% and 12%”. I remember back in the 1970s I bought my first house in a small development in the Finger Lakes area of New York. There were about 30 houses, and there were 3 black families. All was well. Also at this time period I remember reading an article about integration in which the author [based on what I do not remember] stated that 14% black was a tipping point for unrest. I observed this as another black family moved in raising the percentage to 13%. People talked, but tolerantly. A fourth family shifted the tone of the talk,
Perhaps there is more significance to the reported number than would be expected, particularly noting Ohio’s geographic position relative to Michigan during the Civil War.
BTW - my first FIRST
My sense from years ago is that Ohio is more “two states” than Michigan is. Southern Ohio is more aligned with the South, while even parts of northern Michigan, far right wing militia types, is industrial.
OT. Just read this…. Now I’m pissed even more at Raygun.
As the U.S. reflects on the legacy of former President Jimmy Carter, new details from a prominent Texas politician could upend the narrative surrounding one of the defining moments of his presidency: the Iran hostage crisis. According to reporting from The New York Times , former Texas Lt. Gov. Ben Barnes claims that a high-ranking member of Ronald Reagan’s 1980 presidential campaign took him on a secret diplomatic tour of the Middle East in a bid to damage Carter’s re-election campaign by convincing Iran not to release its 52 American hostages until after the election. “History needs to know that this happened. I think it’s so significant and I guess knowing that the end is near for President Carter put it on my mind more and more and more,” said Barnes, 85. After holding the hostages for 444 days in a standoff that derailed Carter’s presidency, Iran finally released them minutes after Reagan was inaugurated on January 20, 1981. Congressional investigations into collusion between the Reagan campaign and Iran did not find evidence of wrongdoing at the time, but Barnes’ account has the potential to shed light on the much-debated episode, which has become known as the “October surprise.”
I always assumed that was common knowledge.
I kinda disagree with this article. IMO, demographics are key to understanidng why OH is going backwards while MI is not. The idea of “demographics” being soley White v. Black is sort of misleading.
I would say this is absolutely central to understanding OH’s descent into MAGA. When some White Union members got this idea that White Union workers weren’t really benefiting from the Union’s activities, that the Union was corrupt (maybe) and that minorities were benefiting more, that’s when they went Right-To-Work. Now, there’s little opportunity for anyone non college degree workers (e.g., manufacturing) and lack of diversity in the workforce doesn’t attract a lot of companies.
In addition, OH has been suffering from brain drain for at least a decade. Factor all these together, and the State hares more in common with the Deep South than States above the Mason-Dixon.